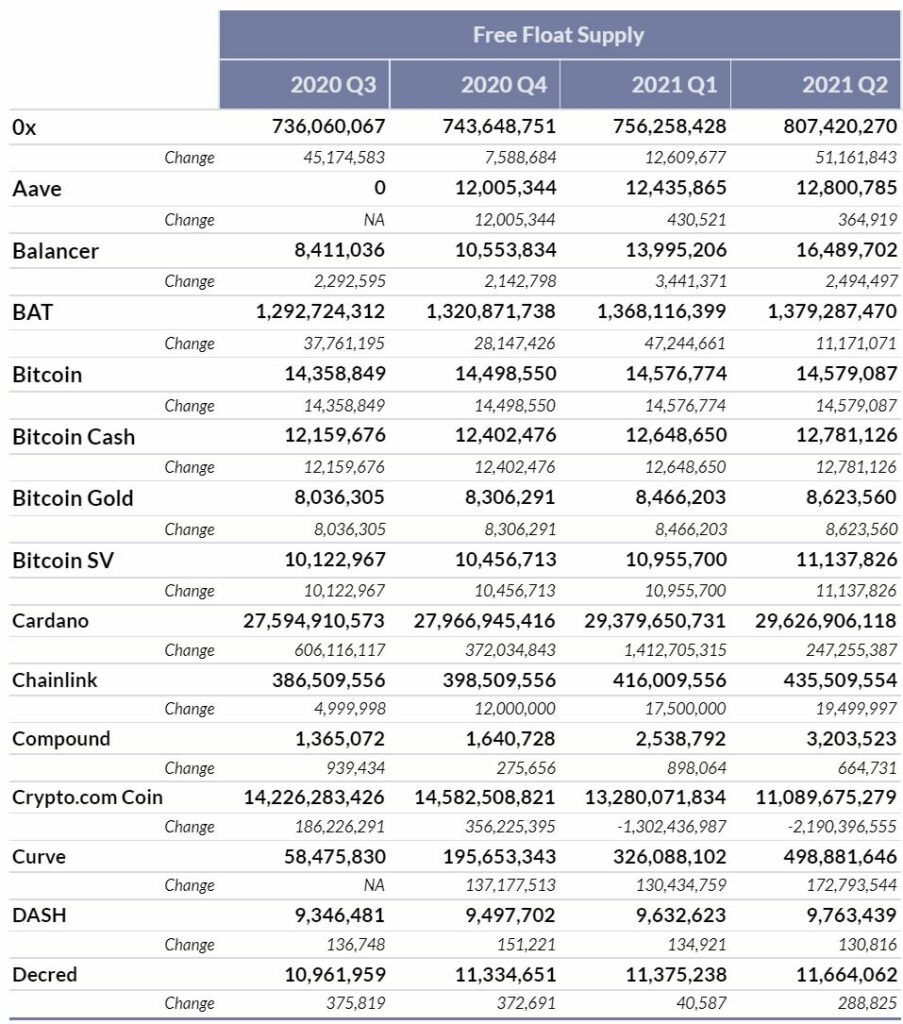
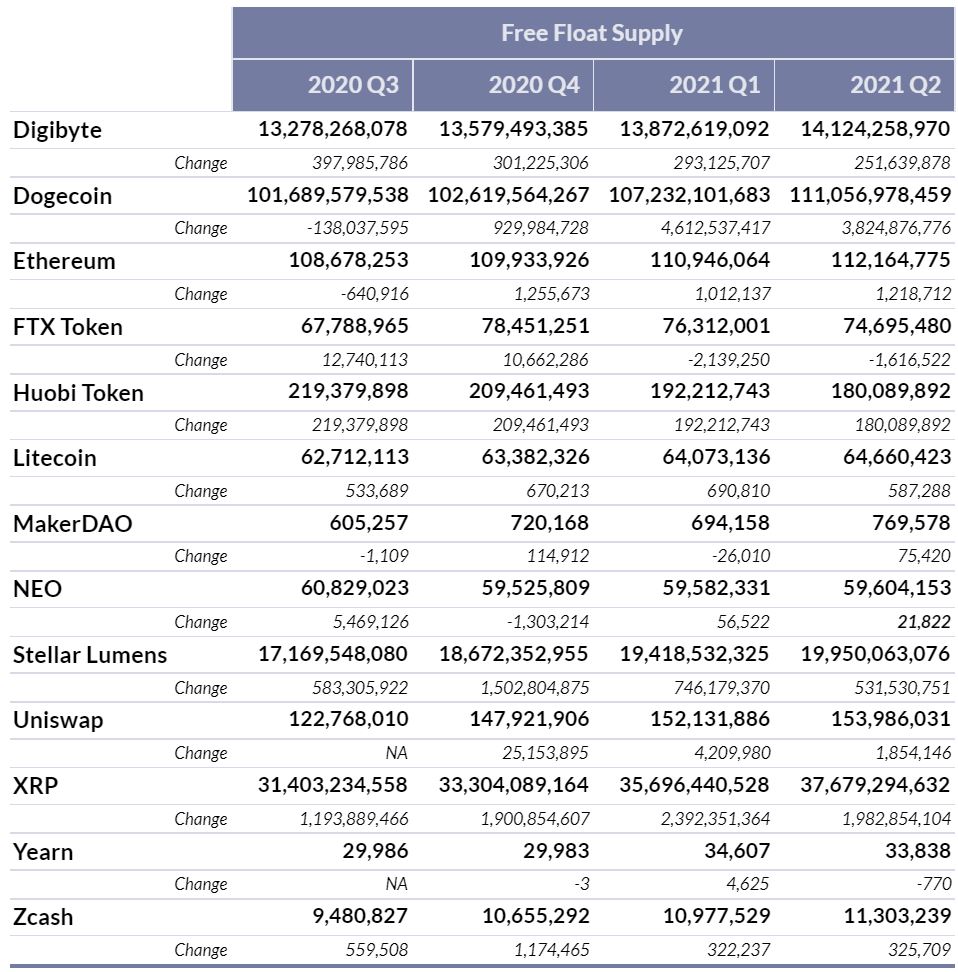
The Supply Transparency Report brings visibility to the actions of the key categories of a cryptoasset’s holders that are deemed to restrict supply from the market, as defined in the CMBI Float Adjustment Methodology. The current universe of cryptoassets that are covered in this report is reflective of those that Coin Metrics administers Free Float Supply values for, which includes: 0x, Aave, Balancer, Basic Attention Token, Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold, Bitcoin SV, Cardano, Compound, Chainlink, Crypto.com Coin, Curve, DASH, Decred, Digibyte, Dogecoin, Ethereum, FTX Token, Huobi Token, Litecoin, MakerDAO, NEO, Stellar, Uniswap, XRP, Yearn and Zcash.
Note, for all of the monthly and quarterly U.S. Dollar values herein, an approximate aggregate quarterly value has been calculated by taking the net supply added or removed each day and multiplying it by that specific date’s Coin Metrics End of Day (00:00 UTC) Reference Rate.
The additional net value added to crypto markets from assets included in this report during Q2 2021 was $10B. This increase is in line with last quarter’s values, but twice that of Q4 2020 and over 5x that of Q3 2020. The most significant reasons for this material increase are over the last 12 months has been:
- The increase in value of most cryptoassets. For example, Bitcoin’s price has increased almost 2.5x since this time last year, meaning that the value of new supply (Bitcoin mined daily) increases by a factor of 2.5. Similarly, other assets experienced significant price increases over the last year, for example Ethereum which is up over 600%.
- Increasing inflation rates of assets as some foundations, teams and long term holders look to access liquidity at attractive prices.
The combination of price increases and new free float added to markets resulted in the largest contributors to the increase in Q2 2021 free float supply value being Ethereum ($4.3B), XRP ($2.3B), Dogecoin ($1.3B), and Stellar Lumens ($640M).
The cryptoassets with the highest free float annual inflation rate (denominated in native units) over the last year were Compound (625%), FTX Coin (36%), MakerDAO (27%), Zcash (26%) and XRP (24%). Over the same period, Crypto.com Coin (-21%), Huobi Token (-18%) and Bitcoin (1.8%) had the lowest annual inflation rate.
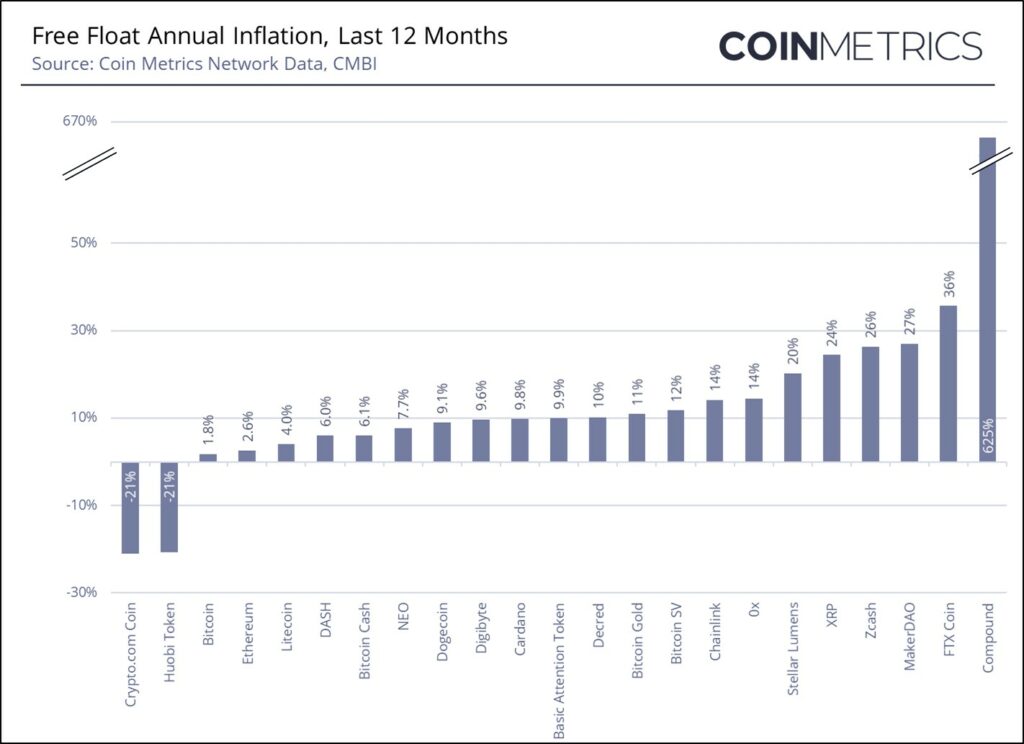
Note: In February and April 2021, Crypto.com conducted a two one off burns of 59.6B and 5B CRO respectively from Foundation controlled addresses
Note: Compound launched in March 2020 with a low initial float and a liquidity mining program that contributed to its high early inflation
FOUNDATION ADDRESSES
The net value of cryptoassets that moved outside of identified Foundation/Company controlled addresses was $3.5B, during Q2 2021, down from $17.1B in the previous quarter. However, if we exclude the Crypto.com Coin burn of $13.3B in Q1, then the supply inflation contribution from Foundation controlled addresses remained relatively flat, decreasing 5% for the quarter. The two largest sources of this quarter’s Foundation token movements can be attributed to:
- The Crypto.com Coin foundation who conducted a second token burn, destroying $1.2B of value from foundation controlled addresses
- The Ripple Foundation who transacted $850M from Foundation controlled addresses
Note: Company/Foundation asset sales can be conducted for many reasons, including but not limited to operating expenses, team member/advisor vesting, strategic long term partnership/BD, scheduled and unscheduled token burns, strategic investments and treasury management. Companies/Foundations may also behave differently, either choosing to issue large volumes infrequently or issue on an as needs basis. Further, movement of assets from Foundation/Company controlled addresses does not necessarily mean assets have been sold (e.g. distribution to team members, burns, strategic placements, community incentive programs, etc).
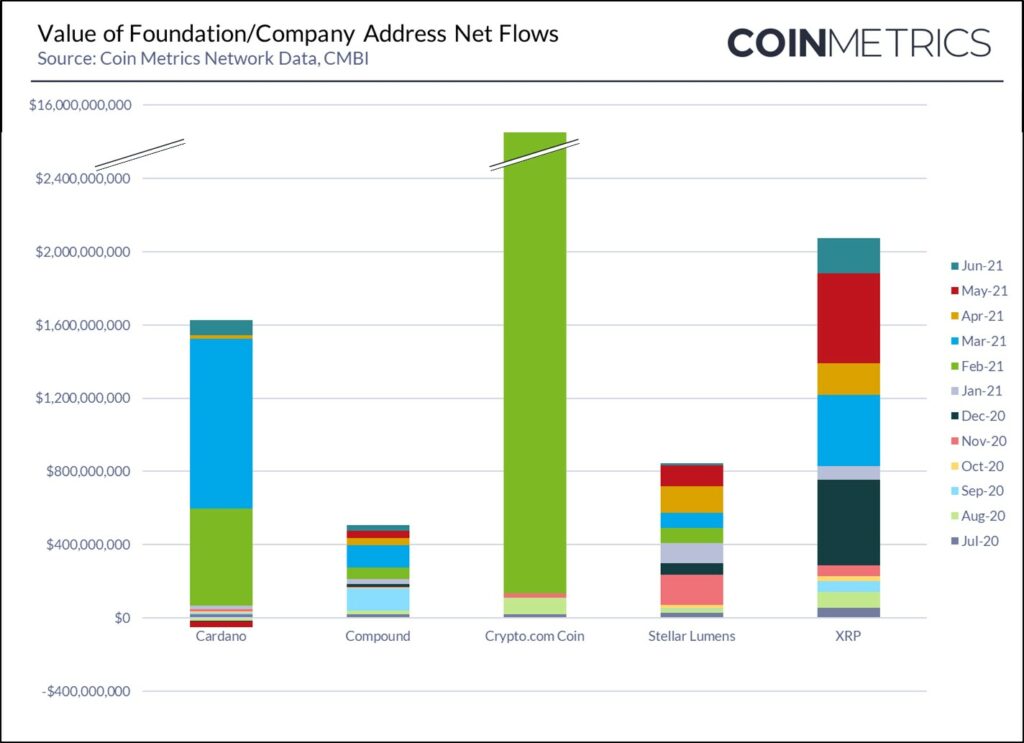
Note: In February 2021, the Crypto.com Foundation burned $13.3B worth of CRO
Note: In April 2021, the Crypto.com Foundation burned $1.2B worth of CRO
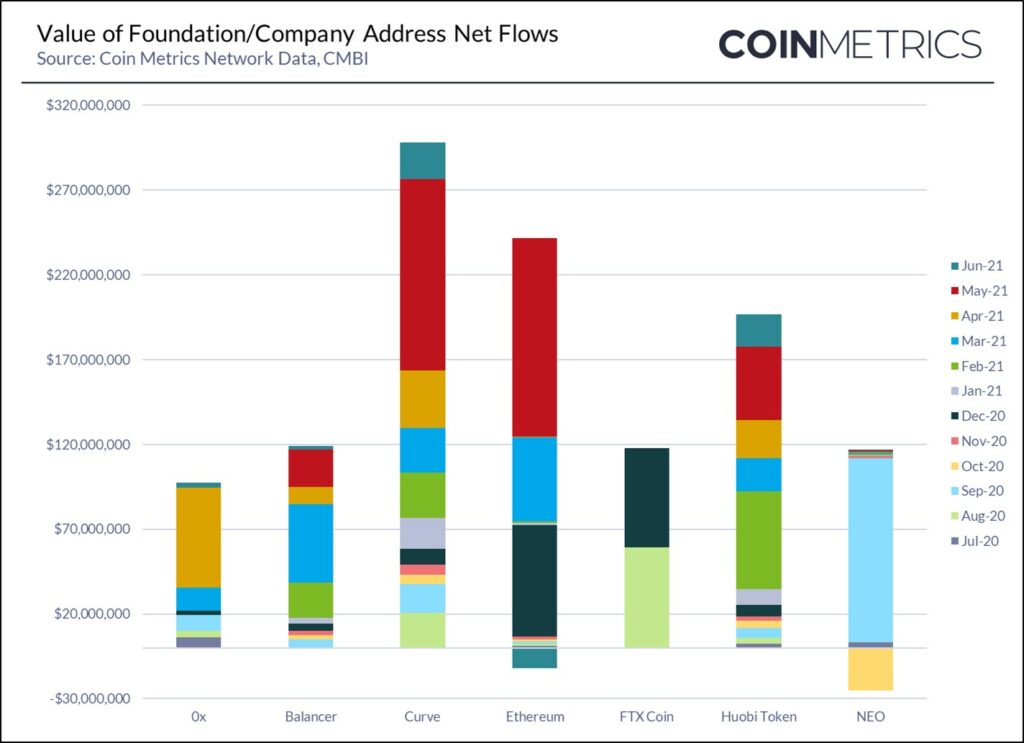
TEAM ADDRESSES
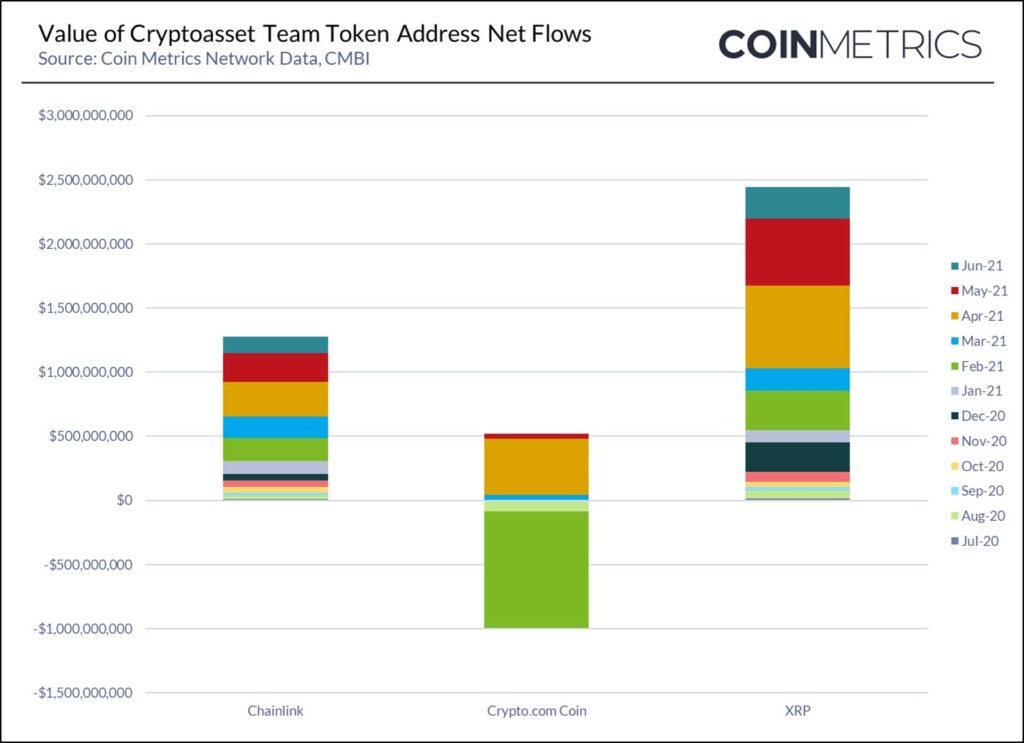
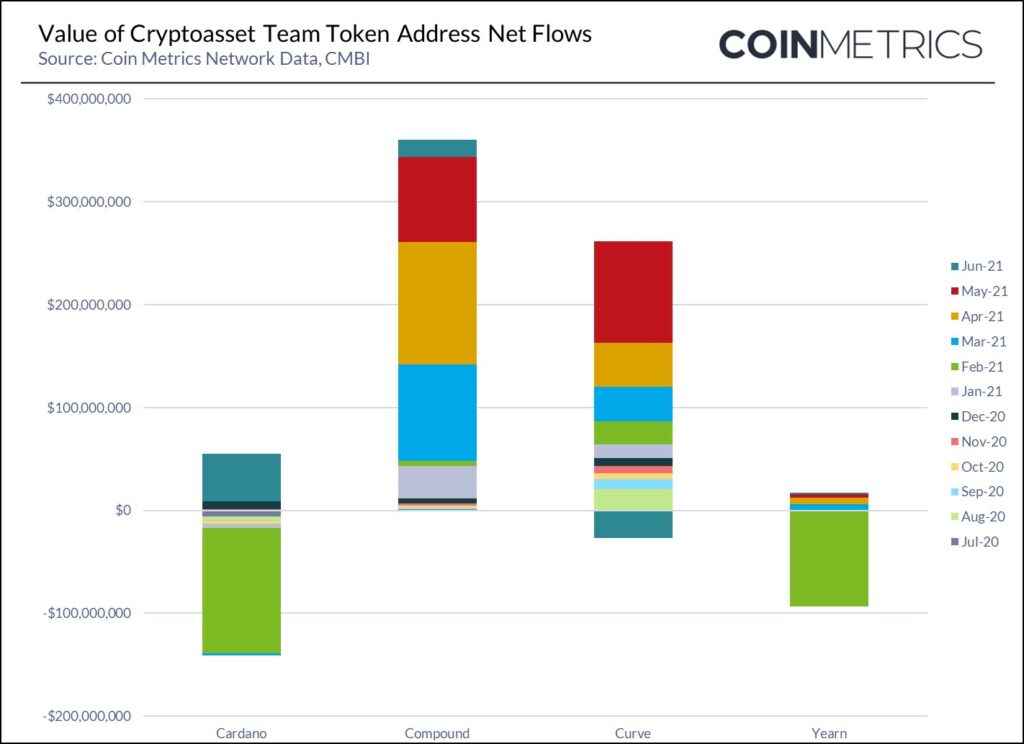
The net value of cryptoassets that moved outside of identified Company Team addresses increased significantly in Q2 2021, up to $3B. The team addresses that most increased to the free float supply of their assets during Q2 2021 were:
- XRP – where an additional 1.2B XRP entered more liquid markets, representing a value of $1.4B
- Chainlink – where an additional 19.5M LINK entered more liquid markets, representing a value of $624M
- Crypto.com – where 2.3B CRO ($480M) left team owned addresses, most of which ended up in the burn wallet and thus did not contribute to the Crypto.com free float supply.
Note: Movement out of Team controlled addresses does not necessarily mean assets have been sold, but rather can be an indication of activity (e.g. movement to passive yield generating tools such as Compound).
SUMMARY OF FREE FLOAT CHANGES
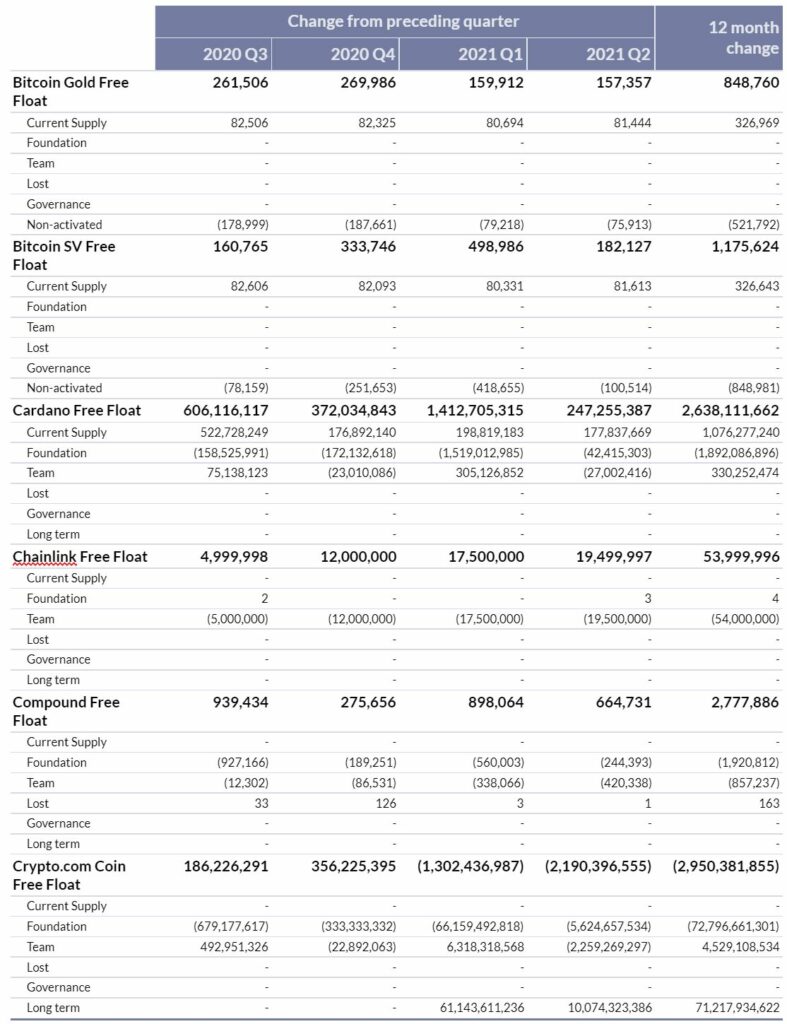
0x (ZRX)
During Q2 2021, the total ZRX moved from Foundation owned addresses was 34M, an increase of 24M from the previous quarter. However, of these, 21M ZRX were deposited into the ZRX vault. As tokens in the vault earn interest, perform governance functions and are indistinguishable from one another, they are considered to be active and thus more liquid than passively held assets. Team owned addresses transacted 16.8M ZRX in Q2, which is significantly more than the previous three quarters in which a combined 4.5M ZRX were moved from team owned addresses. The majority of these however were deposited into Compound and Maker to presumably be used as collateral against loans and/or earn yield.
The net impact of Foundation and Team ZRX transactions was an increase to the free float supply of 41.5M ZRX.
Aave (AAVE)
Having only launched in Q4 of last year, there is limited free float history for Aave. At the end of Q4, Aave owned addresses still managed over 3M AAVE. Of this 3M, just over 500K are still in the Migration contract and unclaimed by LEND holders. AAVE also launched their liquidity mining in Q2 which led to an increased rate of emission from the AAVE DAO which now holds ~2.6M AAVE. Through Q2, there was a free float increase of 365K AAVE.
Balancer (BAL)
Balancer released 1,885,000 BAL tokens into circulation through their liquidity mining program, mimicking the same numbers from Q4 of 2020. The number of BAL released from the Balancer Foundation into more liquid markets reduced in Q2, with only ~725K BAL transacted from Foundation controlled addresses, down from 1.7M BAL in Q1. With a small net accumulation of 117K BAL tokens in team owned addresses, the net change to free float through the Q2 2021 was 2.5M.
Basic Attention Token (BAT)
Throughout Q2 2021, the quarterly increase of Basic Attention Token free float was its lowest over the last year. Only 11.2M new BAT entered circulation in Q2, down from 47.1M in the previous quarter. The majority of the reduction came from less activity from foundation controlled wallets, the most active being the ‘BAT: UPG Reserve’, which only had a net outflow of 6M BAT, significantly less than the previous three quarters where there were outflows of 26.5M (Q1 2021), 28.8M (Q4 2020) and 24.7M (Q3 2020).
Identified team addresses made up for the remaining increase to free float, with an 4.4M BAT entering more liquid markets, down from Q1 2021’s outflow of 20M BAT.
Bitcoin (BTC)
The new Bitcoin issued from mining activities in Q2 2021 was 75.2K, slightly lower than previous quarters and what is expected from the 10 minute block issuance target. The primary reason for this was the significant reduction in hash rate as Chinese miners went offline in response to new regulations and enforcement in the region. This led to less blocks being produced, and thus a lower rate of inflation for the quarter. However, during the quarter 73K BTC aged to over 5 years without activity. As per the Free Float Methodology, these coins are classified as likely belonging to strategic long term holders or as being lost, thus not contributing to liquid markets (and free float).
This resulted in a net free float increase of only 2K BTC for the quarter.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Changes to Bitcoin Cash’s free float was ~100K BCH lower than the previous two quarters. Whilst the emissions from mining in Q2 were in line with the previous two quarters, only 50K BCH entered free float supply from coins activated for the first time since Bitcoin Cash forked from Bitcoin, down from ~160K in the previous quarters.
This resulted in a net free float increase of 132K BCH for the quarter.
Bitcoin Gold (BTG)
Bitcoin Gold’s free float increased 157K BTG throughout Q2 of 2021, in line with Q1’s levels but over 100K lower than the increases in both Q3 and Q4 2020. 81K BTG were added to the free float from mining activities, with an additional 76K BTG added to the free float of Bitcoin Gold came from coins that were activated for the first time since the BTG fork.
This resulted in a net free float increase of 157K BTG for the quarter.
Bitcoin SV (BSV)
Bitcoin SV’s free float supply increased 181K BSV during Q2 2021, down significantly from Q1 2021 where 498K BSV were added to free float. Whilst the new issuance of Bitcoin SV from mining related activities was in line with previous quarters, only 100K BSV were activated for the first time since the BSV fork, the lowest quarterly increase in activated supply since Q3 of 2020.
This resulted in a net free float increase of 182K BSV for the quarter.
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano’s free float increased 247M ADA in Q2 2021, down significantly from Q1’s record free float supply quarterly increase of 1.5B ADA. The majority of this quarter’s increase was the result of the proof of state mining emissions which added 178M ADA to the on chain supply of Cardano.
Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink’s free float supply increased for the third consecutive quarter, experiencing its largest quarterly increase since Q3 2019, with an additional 19.5M LINK added during Q2 2021, up from 17.5M in Q1. The entirety of the increase in free float supply can be attributed to transactions from team identified addresses.
Compound (COMP)
During Q2, 665K COMP were added to free float supply, a reduction of 26% from Q1 (898K). Foundation controlled addresses released 56% less COMP during the quarter, with only 244K COMP released into more liquid markets, primarily through liquidity mining emissions. However, team controlled addresses gain increased, with 420K COMP leaving closely held team controlled addresses, up from 388K in Q1 and 87K in Q4 2020. This could be the result of vesting tokens as the protocol is now over a year old.
Crypto.com Coin (CRO)
During Q2 of 2021, the Crypto.com Foundation conducted another significant burn from the CRO foundation holdings, destroying 5B CRO on Apr 01 by sending them to the 0x000…00dead address. As this came from Foundation controlled addresses, the burn did not impact the free float of CRO, but rather represented a change to the future total maximum supply of CRO.
2.3B CRO in team controlled addresses tokens were burned and sent to the 0x000…00dead address during the quarter. On top of this, a further 2.1B CRO that was included in the free float was burned during the quarter, some coming straight from the Bittrex exchange.
The net impact of all these changes was a reduction in CRO free float supply of 2.2B, its second consecutive quarterly decrease in free float.
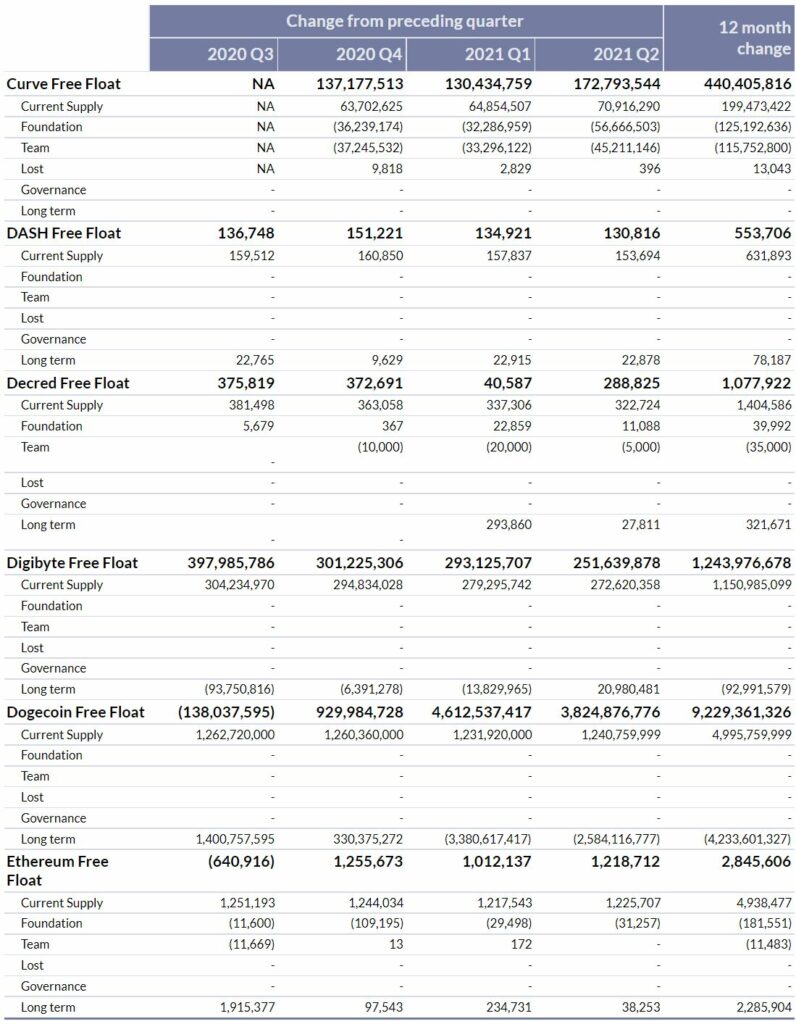
Curve (CRV)
The free float supply of Curve increased by 173M CRV in Q2 2021, slightly higher than the previous two quarters which saw an increase of 130M (Q1 2021) and 137M (Q4 2020). Curve is a relatively new protocol that launched in August of 2020 and has a predefined rate of token issuance that is set to continue at a similar pace for the next few quarters. The majority of the increase in free float supply was from increased issuance of tokens from foundation controlled addresses to liquid markets and the release of team controlled CRV .
DASH (DASH)
DASH’s issuance from mining related activities in Q2 was 154K DASH, in line with previous quarters which were after the ~6.0% inflation rate adjustment that occurred during Q2 of 2020. During the quarter, there were 23K DASH that were identified as being inactive for over 5 years and as belonging to long term strategic investors or lost supply. The net result of the two aforementioned factors was an increase in DASH’s free float supply of 131K for the quarter.
Decred (DCR)
289K DCR was added to the Free Float Supply during Q2 2021, an increase from Q1’s record low free float increase (40K). The majority of the increase resulted from the 323K DCR that were added to the total on chain supply from mining activities during the quarter, with 28K and 11K DCR being removed from supply due to aging (>5yrs old) and foundation accumulation.
Digibyte (DGB)
The Free Float Supply of Digibyte increased 252M DGB in Q2, a decrease of 14% from Q1. Inflation from Digibyte mining related inflation continues to decrease every quarter, with 273M added this quarter, down from 279M in Q1. There were also 21M DGB that were removed from free float during the quarter as they aged over 5 years without activity. As per the Free Float Methodology, these coins are classified as likely belonging to strategic long term holders or as being lost, thus not contributing to liquid markets (and free float).
Dogecoin (DOGE)
Dogecoin’s free float again increased relatively significantly during Q2 of 2021 after addresses holding 2.6B DOGE that had not been active in over 5 years transacted. Along with the 1.2B new DOGE on-chain supply from mining activity, Dogecoin’s net free float increase for the quarter was 3.8B.
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum’s free float increased 1.2M ETH in Q2 of 2021, with the vast majority of new supply (1.2M) coming from block subsidies for miners (1.2M). There was also 31K ETH that was moved from Foundation held addresses to more liquid markets, which was offset by the 38K ETH that was removed from free float supply as a result of long term, strategic holders or lost assets that have not been transacted in over 5 years.
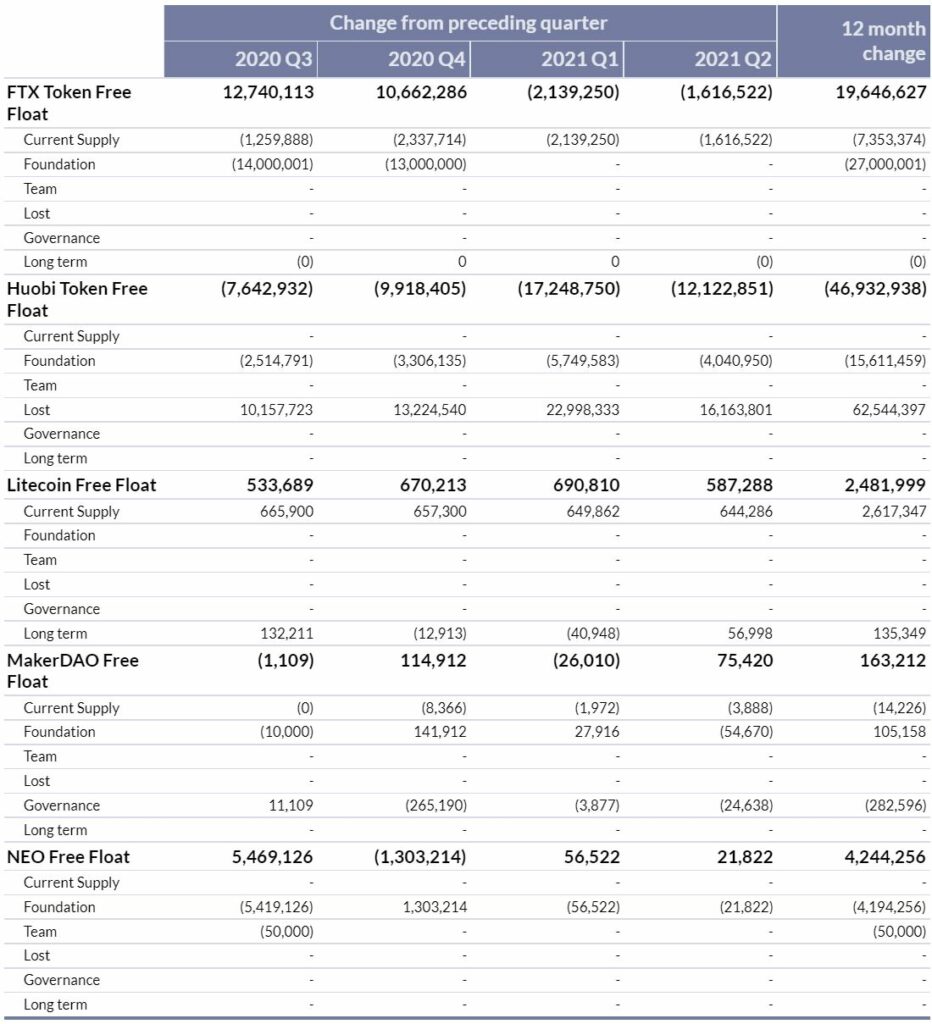
FTX Token (FTT)
During Q4, the free float supply of FTX Token fell for the second quarter running. This was the result of 1.6M FTT being burned (sent to the 0x000 address). Q2’s burn was 24% lower than Q1’s burn of 2.1M FTT. In Q2 2021, there was no team or foundation FTT added to more liquid addresses, resulting in a reduction of the free float supply of FTT by 1.6M during the quarter.
Huobi Token (HT)
Huobi Token continues to be one of the most consistent deflationary assets in the crypto market, recording a reduction in free float supply every quarter of 2020. During Q2, this did not change, with the HT free float supply reducing by 12.1M. This was comprised of:
- Huobi continued to conduct on-chain burns of HT, sending tokens to the 0x000…000 address which received 16.2M HT during the quarter.
- The Huobi Foundation transacting 4.0M HT from foundation owned addresses into more liquid markets.
Litecoin (LTC)
Litecoin’s free float supply increased 587K LTC during Q2, which is generally in line with previous quarterly increases. Whilst the new supply from mining related activity remained relatively consistent, adding 644K LTC in Q2, a net increase to LTC in addresses that have remained dormant for over 5 years (57K) removed some liquidity from markets. The net result was an increase in free float supply of 587K LTC during Q2 2021.
MakerDAO (MKR)
The free float supply of MakerDAO returned to a net increase in Q2 2021, with 75K MKR added to the free float. The primary reason for this increase was due to the 55K MKR being removed from the MakerDAO Governance contract.
In addition to this, MakerDAO also experienced a reduction in on chain supply, with 3.9K MKR bought back from DAI generated fees and burned during the quarter.
NEO (NEO)
The NEO free float supply increased by 21.8K in Q2 of 2021, the total balance coming from Foundation owned NEO that were moved to more liquid addresses during the quarter.
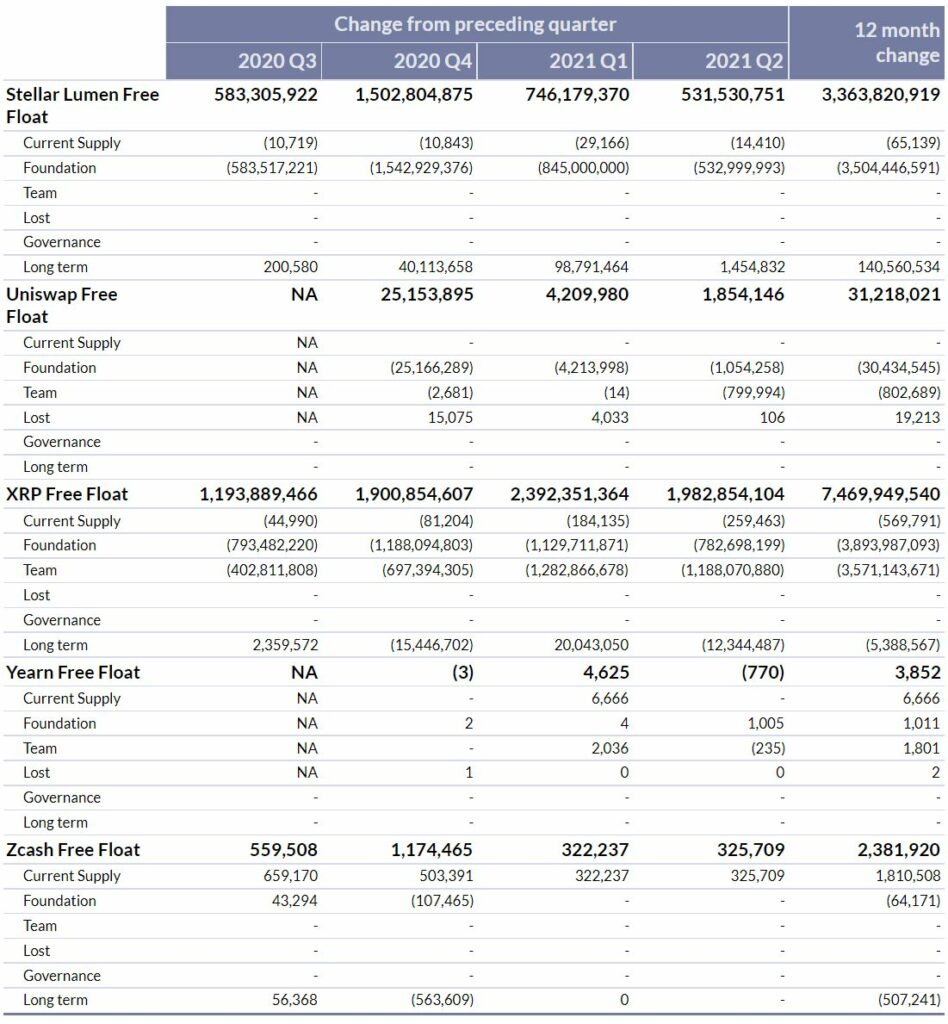
Stellar Lumens (XLM)
The Stellar Lumen free float supply increased 532M XLM during Q2 2021, a 29% reduction from the previous quarter. The entirety of the increase in free float can be attributed to Foundation owned addresses moving XLM to more liquid addresses during the quarter.
Uniswap (UNI)
The free float supply of Uniswap increased by 1.0M UNI during Q2 2021. This increase in free float supply came wholly from users still claiming their airdrop from the UNI distribution address for the first time.
XRP (XRP)
The XRP free float supply increased 2.0B during Q2 2021, which is largely in line with their previous two quarters. The largest contributor of extra liquidity to the market during the quarter was from Ripple Team addresses, which experienced net outflows of 1.2B XRP, an increase of 4x since Q2 of 2020. Ripple Foundation addresses also experienced a 0.8B XRP net outflow.
Yearn (YFI)
During Q2 of 2021, Yearn’s free float supply decreased 770 YFI. The majority of this came from the increase of YFI held in team identified addresses, most of which came in from deployed treasury assets that were in Yearn Vaults.
Zcash (ZEC)
Zcash free float supply increased 326K ZEC during Q2 2021, very similar to last quarter’s increase which was the smallest quarterly free float increase historically. This low level again is the result of the recent ZCash block halving event in November of 2020.
There were no other known changes to the free float supply of Zcash. Note it is unknown if the foundation/team control assets if they utilize shielded transactions (privacy works!).
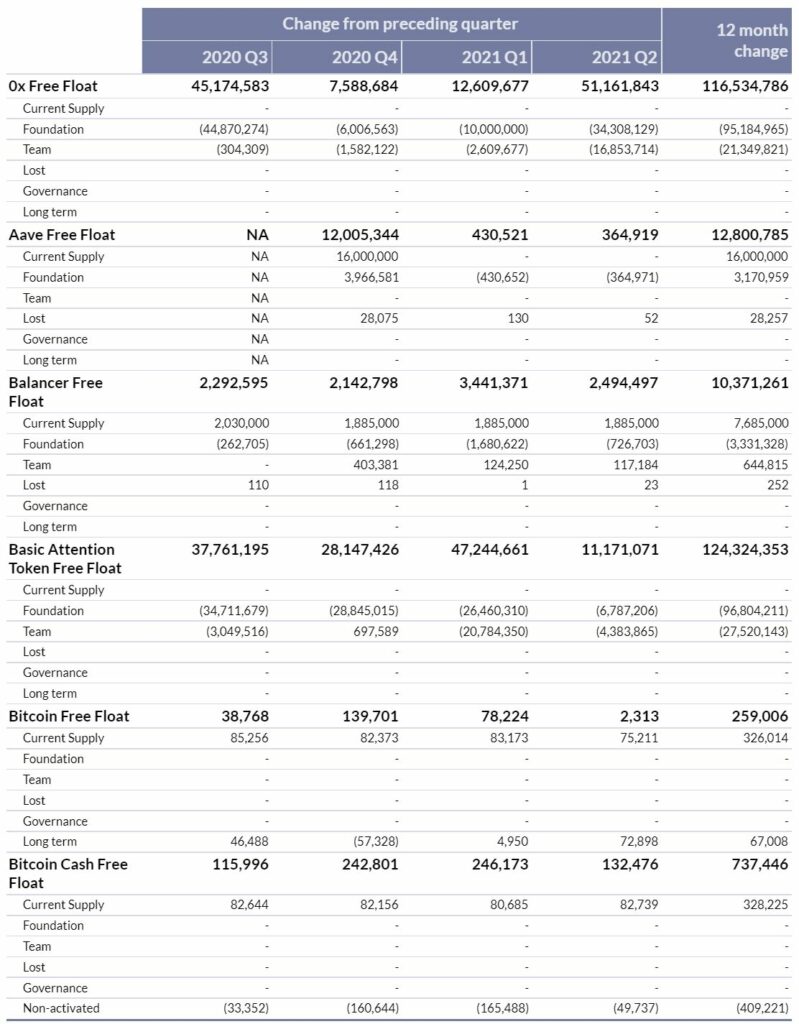
DETAILED FREE FLOAT BREAKDOWN
ABOUT COIN METRICS
Coin Metrics is a leading provider of transparent and actionable cryptoasset market and network data. Coin Metrics delivers mature data across multiple formats to various industry stakeholders, including financial enterprises, funds, media and research outlets, and data/application providers. Coin Metrics’ data empowers its clients and the public to better understand, value, use, and ultimately steward public crypto networks. Further Coin Metrics research can be found here.
ABOUT CMBI
Coin Metrics launched CMBI to bring independent and transparent index solutions to the cryptoasset investment community. In the nascent and often complex cryptoasset market, CMBI Indexes strive to be dynamic and adjust to the rapidly changing market conditions to design and maintain investable products. CMBI Indexes provide markets and customers with industry-leading solutions that aid in performance benchmarking and asset allocation.
